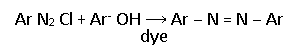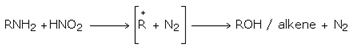Nitrous Acid Test,Separation of primary , secondary and tertiary amines by Hoffmann's method: Amines
Test of 10, 20 and 30 amines. (nitrous acid test)
The three classes of amines react differently with nitrous acid.
Nitrous acid is a source of electrophilic nitrosonium ion (O = N+), which reacts with amines. Nitrous acid being unstable is generated in situ from a mineral acid and sodium nitrite.
Primary aromatic amine reacts with nitrous acid to form a diazonium salt which is stable but low temperatures.
On reaction with phenol, an aromatic diazonium salt undergoes a coupling reaction to form a dye.
Primary aliphatic amines form diazonium salts which are unstable and liberate nitrogen to form a carbonium ion which in aqueous reaction medium forms an alcohol or on proton elimination gives an alkene.
So primary amines liberate N2 with nitrous acid unlike 2o and 3o amines. So this can be used to distinguish 1o amines from 2o and 3o amines.
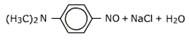
Secondary amines, both aliphaptic and aromatic on reaction with nitrous acid give yellow colored oily N-nitrosoamines which unlike amines are insoluble in aqueous mineral acids. This is used as a test for 2o amines.
R2 NH NaNO2 + HCl → R2 N – N = O + NaCl + H2O
Aliphatic tertiary amines form water soluble salts with nitrous acid.
Aromatic tertiary amines on reaction with nitrous acid, undergo electrophilic substitution with nitro sonium ion at the p-position of the phenyl ring.
|
Test |
Primary amine |
Secondary amine |
Tertiary amine |
|
Action of CHCl3 and alcoholic KOH. (Carbylamine test) |
Bad smelling carbylamine (Isocyanide) is formed. |
No action. |
No action. |
|
Action of CS2 and HgCl2. (Mustard oil test) |
Alkyl isothiocyanate is formed which has pungent smell like mustard oil. |
No action. |
No action |
|
Action of nitrous acid. |
Alcohol is formed with evolution of nitrogen. |
Forms nitrosoamine which gives green colour with phenol and conc. H2SO4 (Liebermann’s test). |
Forms nitrite in cold which on heating gives nitrosoa- mine which responds to Liebermann’s test. |
|
Action of acetyl chloride. |
Acetyl derivative formed. |
Acetyl derivative is formed. |
No action. |
|
Action of Hinsberg’s reagent. |
Monoalkyl sulphonamide formed which soluble in KOH. |
Dialkyl sulphonamide is formed which is insoluble in KOH. |
No action. |
|
Action of methyl iodine. |
3 molecules (moles) of CH3I to form quaternary salt with one mole of primary amine. |
2 moles of CH3I to form quanternary salt with one mole of secondary amine. |
One mole of CH3I to form quaternary salt with one mole of tertiary amine. |
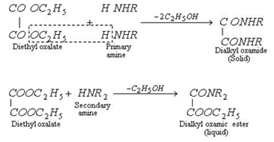
Separation of primary , secondary and tertiary amines by Hoffmann's method
The mixture of three amines is treated with diethyl oxalate. The primary amine forms a solid oxamide, a secondary amine gives a liquid oxamic ester while tertiary amine does not react.
Primary amine is recovered when solid oxamide is heated with caustic potash solution and collected as distillate on distilling the reaction mixture.
The liquid (mixture of oxamic ester+ tertiary amine) is subjected to fractional distillation when tertiary amine distils over.
The remaining liquid is distilled with KOH to recover secondary amine.
 SureDen
SureDen