Seeds and its Types
Seeds and its types
Seeds
The fertilized ovule forms seed. The study of seed of called Spermology .The seeds are of two types ;
- Non- Endospermic or Exalbuminous Seeds
In seeds like gram, pea, groundnut, the endosperm is completely consumed by the embryo, thus the seeds are called non-endospermic or exalbuminous e.g., dicots.
The outer seed coat is called testa and inner seed coat is called tegmen. The food is stored in the Cotyledons.
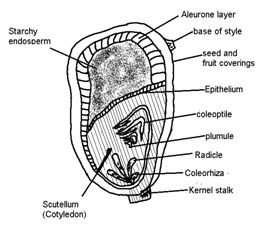
- Endospermic or Albuminous seed
In monocots and castor bean (dicots) embryo does not consume all endosperm. So it persists in the mature seed. Such seed are called endospermic and albuminous seeds. In these seeds food is stored in endosperm. In monocot seeds, the membranous covering present around radical is called coleorrhiza and aroud plumule is called coleoptiles (e.g., Maize).
- Perispermic seeds : Mostly nucellus is consumed after fertilizatilon due to absorption of food by the endosperm and embryo. The remains of nucellus in the seed is called perisperm. Such seeds are called perispermic seeds e.g., Piper nigrum (Black Pepper).
- Chalazosperm : Is perisperm like tissue in chalazal region. It is a substitute for endosperm e.g., Cynastrum.
Important Points
- DIcot plants like Calophyllum, Eryngium have parallel venation.
- Monocot plants like Smilax, Dioscorea and aroids have reticulate venation.
- Stimulate are at the base of a base whereas stipels are at the base of a leaflet.
- Cauliflory is appearance of floral bubs on the stem e.g. Jackfruit.
- Nest roots are adventitious roots of Dischidia a non-insectivorous Pitcher Plant.
 SureDen
SureDen