Properties of Colliadal Solutions
Properties of colloidal solutions:-
The main properties of the colloidal solutions are discussed below:-
- Physical properties:-
- Heterogeneous character:- The colloidal solutions are heterogeneous in nature. They consists of two phase dispersed phase and dispersion medium. their heterogeneous character is clearly visible under electron microscope.
- Stable nature:- The colloidal solutions are quite stable. Their particles are in the state of continuous motion and do not settle down at the bottom of container.
- Filterability:- the colloidal particles can be filtered through semipermeabale membrane or the ultra filter papers.
- Colligative properties:- Osmotic pressure:- due to the high average value of the molar mass of the colloids the value of collegative properties is very small, however the colloidal solution have measurable value of Osmotic pressure which is used in the measurement of average molar mass.
- Mechanical properties (Brownian movement):-
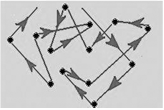
Brownian observed that when viewed through an ultra microscope colloidal particles are seen continuously moving in a zig-zag way which is called Brownian movement. Hence “Brownian movement may be defined as continuous movement of colloidal particles in a colloidal sol.”
It is due to the reason that the molecules of dispersion medium are in the state of continuous motions and strike the colloidal particles from all sides with different forces causing them to move. However due to the heavy mature of the colloidal particles do not settle down as Brownian movement opposes the gravitation force.
3. Optical properties:- Tyndall Effect:- If a beam of light is passed through a colloidal sol. Placed in a darkroom, the path of light becomes visible (bluish illuminated when viewed from a direction at right angle to that of incident beam.
The visibility of light beam is due to the scattering of light by the colloidal particles. The effect was studied by Tyndall and hence is known as Tyndall Effect. Thus Tyndall effect may be defined as, “The phenomenon of scattering of light by colloidal particles as a result of which the path of the beam becomes visible is called the Tyndall effect.
4. Electrical Properties:- the colloidal particles being having a specified charge show electrical properties. These are:
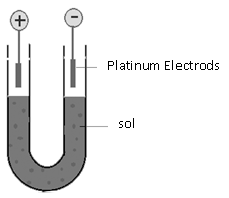
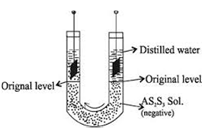
a) Electrophoresis: If the colloidal particles possess a net charge over it. It can be shown by an experiment that when the colloidal solutions are subject to some electrical field their colloidal particles start moving toward the oppositely charged electrode. This movement of the colloidal particles is called “Electrophoresis”. Thus the movement of colloidal particles towards oppositely charged electrodes under the influence of an electric field is called electrophoresis.” Earlier the word cataphoresis was used as the sols studied at that time were the positively and negatively charged sols are known hence the word Electrophoresis is used.
b) Electro-osmosis:- In the electrophoresis tube if semi permeable membrane is put near the electrodes, there will be the movement of dispersion medium particles through the semi permeable membrane. The movement of dispersion medium from the colloidal solution through SPM under the influence of electric field is called Electro-osmosis.
- Coagulation or Flocculation or Precipitation of sol:- It is the process which involves coming together of colloidal particles so as to change into large sized particles which ultimately settle as a precipitate. Coagulation may be brought about by
- Mutual neutralization i.e. by mixing two oppositely charged solutions.
- By the process of Electrophoresis
- Prolonged Electro-osmosis
- By addition of electrolytes.
Out of the above methods of coagulation addition of electrolytes is the most important used method. On addition of an electrolyte the charge on the colloidal particle is neutralized by the oppositely charged ions and the neutral particles then accumulate to form large sized particles which settle down. The coagulating power of an electrolyte is given by Hardy Schulze Rule. According to this rule, “Greater the valence of oppositely charged ion of electrolyte being added, the faster is the co-agultion.” Thus for coagulation of the negatively charged solution the co-agulating power of different ions is in the order Al+3 > Ba+2 > Na+ and for the coagulation of positively charged solution the co-agulation power of different ions is in the order PO4-3 > SO42- > Cl-
The minimum amount of an electrolyte (in milimoles) that must be added to one liter of a colloidal solution so as to bring about complete co-agulation is called co-agulation value of an electrolyte greater is its co-agulation of precipitating power.
Protective action of lyophilic colloids (GOLD NUMBER):-
Lyophobic sols are unstable and are easily precipitated. These sols can be stabilized by the addition of a small amount of lyophilic solution e.g. galatin solution is added to Gold sol to stabilize Gold sol. This process of protection of lyophobic sol by addition of lyophilic sol is called protective action of a lophilic sol. The protective power of different colloids is measured in terms of Gold Number defined as, “Gold number is the minimum amount of any protective colloid in milligrams which must be added to a 10 ml standard red gold sol so that no co – agulation of gold solution occur when 1 ml of 10% NaCl solution is added to it.” Thus smaller the value of gold number for a protective colloid greater is its protective power.
 SureDen
SureDen