Human male reproductive system
Human male reproductive system:
The male reproductive system consist of the following:
- Primary sex organs: Testis
- Accessory ducts: Rete testis, Vasa efferentia, epididymis and vas deferens.
- Accessory glands: Seminal vesicle, prostate and bulbourethral glands.
- External genitalia: Penis.
Male reproductive system:
a) Testis:
- The testes are situated outside the abdominal cavity within a pouch called scrotum. The scrotum helps in maintaining the low temperature of the testes (2–2.5o C lower than the normal internal body temperature) necessary for spermatogenesis.
- In adults, each testis is oval in shape, with a length of about 4 to 5 cm and a width of about 2 to 3 cm.
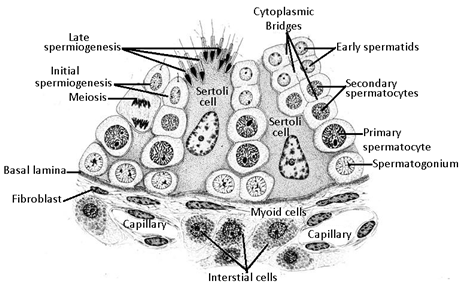
- Each testis has about 250 compartments called testicular lobules. Each lobule contains one to three highly coiled seminiferous tubules in which sperms are produced.
-
Each seminiferous tubule is lined on its inside by two types of cells called male germ cells
(spermatogonia) and Sertoli cells. - The male germ cells undergo meiotic divisions finall leading to sperm formation, while Sertoli cells provide nutrition to the germ cells.
- The regions outside the seminiferous tubules called Interstitial Spaces, contain small blood vessels and interstitial cells or Leydig cells.
- Leydig cells synthesise and secrete testicular hormones called Androgens.
Seminiferous tubules:
b) Accessory duct system:
- The seminiferous tubules of the testis open into the vasa efferentia through rete testis.
- The vasa efferentia leave the testis and open into epididymis located along the posterior surface of each testis.
- The epididymis leads to vas deferens that ascends to the abdomen and loops over the urinary bladder. It receives a duct from seminal vesicle and opens into urethra as the ejaculatory duct. These ducts store and transport the sperms from the testis to the outside through urethra.
- The urethra originates from the urinary bladder and extends through the penis to its external opening called Urethral Meatus.
c) Acccessory glands system:
The male accessory glands include paired seminal vesicles, a prostate and paired bulbourethral glands.
- Prostate glands: Secretes a milky secretion containing citric acid, lipids, and enzymes, Which nourishes and activates the sperms to swim.
- Seminal vesicles: Secretes mucus and a watery alkaline fluid, that contain fructose for providing motility to sperm.
- Bulbourethral glands or Cowper’s gland: Secrete mucus that helps in the lubrication of the penis by its secretion.
d) Penis (The external genitalia):
- The penis is the male external genitalia. It is made up of special tissue that helps in erection of the penis to facilitate insemination. The enlarged end of penis called the glans penis is covered by a loose fold of skin called Foreskin.
Related Keywords
 SureDen
SureDen