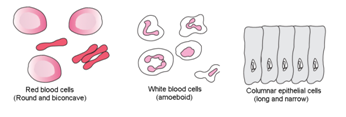
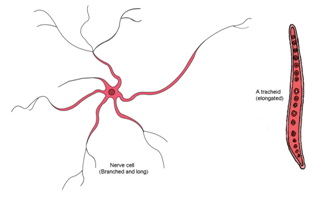
Cell membrane
Cell Membrane (J.O. Plowe (1931) called it plasmalemma):
- Its presence was first recognised by Naigeli & Cramer who gave the term ‘plasma membrane’
- Gorter and Grendel (1925) postulated that it is made of “bimolecular lipid layer”.
- 1) A thin, delicate membrane of about 70 Å to 100 Å thickness made almost entirely of proteins and lipids. The most common lipids are Phospholipids.
2) Each phospholipid molecule consists of a polar head containing phosphate, and two non-polar hydrocarbon tails from the fatty acids used make the molecules.
3) The head is hydrophilic (water –loving) and the tails are hydrophobic (water-hating) in presence of water they form a bilayer.
4) Membrane proteins have been classified as Integral (Intrinsic) or Peripheral (extrinsic) according to the degree of their association with the membrane and the methods by which they can be solubilized.
5) Peripheral proteins are separated more than 70% of the membrane proteins and require drastic procedures for isolation. e.g. spectrin of erythrocytes, cytochrome c of mitochondria.
6) Integral Proteins represents more than 70% of the membrane proteins and require drastic procedures for isolation. e.g. most membrane bound enzymes, drug and hormone receptors, histocompatibility antigens (glycophorins).
 SureDen
SureDen